

5 Mbit/s Near-Field Links at Sub-Milliwatt Power
Contained electric fields of Near-Field Electric (NFE) keep communication near the device for fast predictable interaction within arm’s reach
<1 mW
Rx/Tx power @ 5 Mbit/s
5 Mbit/s
2025 data rate; H1 2026: 20 Mbit/s
<1 ms
Wire-like low latency
5–25 cm
Range between devices
How NFE works
Wi-R NFE uses a contained electric field to couple two powered devices at close range. Signal stays near the device, creating a physically local link that feels immediate and avoids room-scale broadcast. Requires touch or near-touch coupling(typical operation within a few centimetres, with exact range depending on electrodes and environment).
Read White Paper (arXiv preprint)Evidence for design decisions
Low Power, Close Range
Lowest device power at contact-range coupling
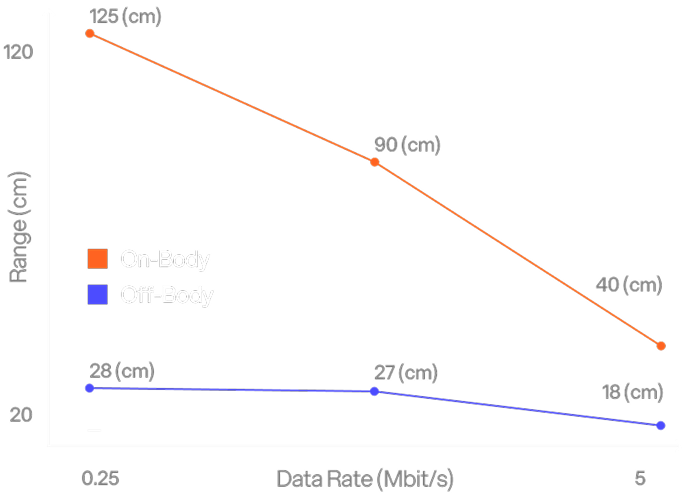
Configurable Range
Range varies with orientation and data rate

Along-Conductor Communication
Conductive surfaces can extend effective touch or near-touch coupling
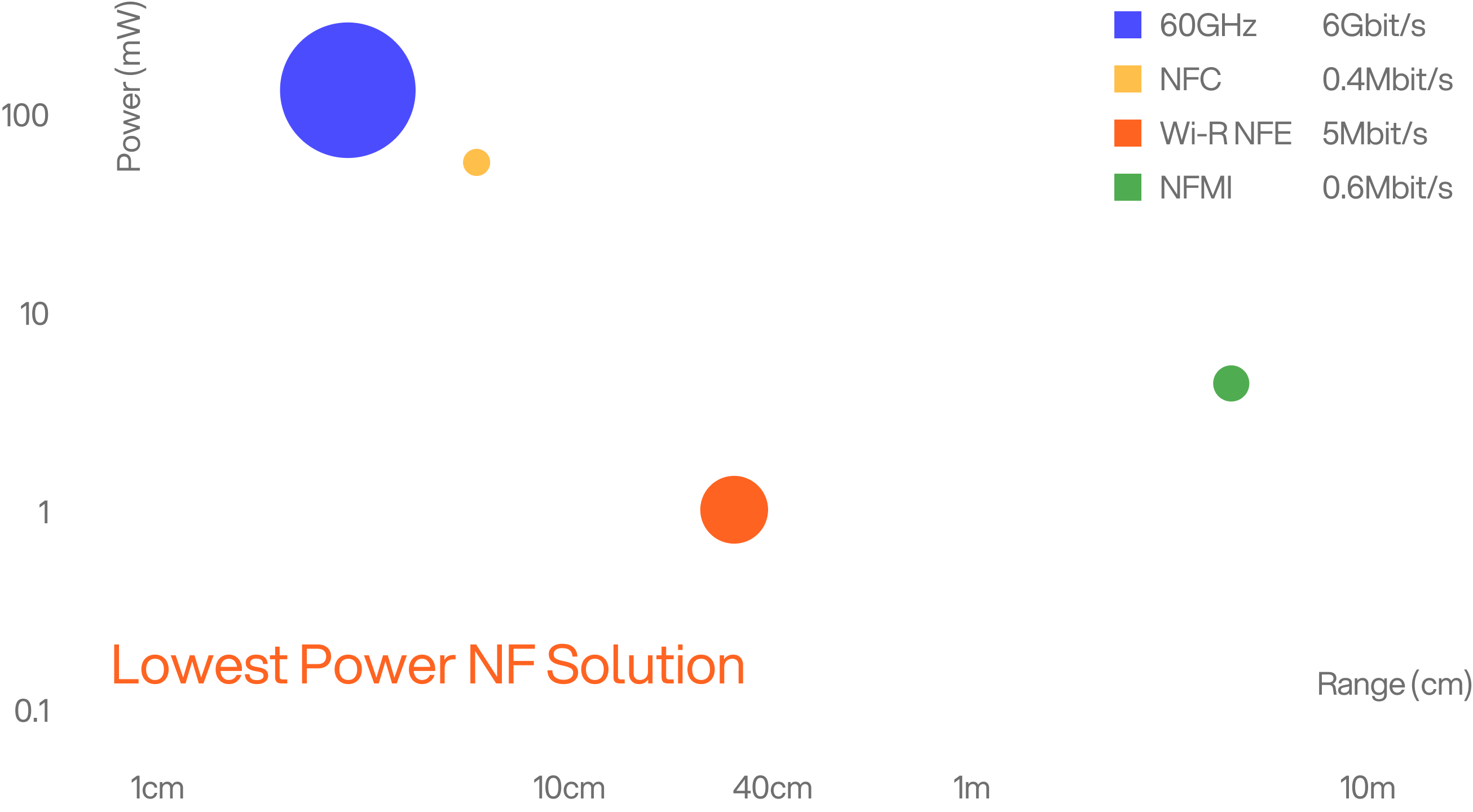
How NFE compares to near-field alternatives
| Tech | Typical Power | Data Rate | Range | Best Fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-R NFE | sub-milliwatt class | 5 Mbit/s | 5-30cm | Provisioning, sealed devices, local data |
| NFC | reader high, endpoint passive | ~0.4 Mbit/s | ~4 cm | Payments, tap |
| NFMI | mW-class | ~0.6 Mbit/s | ~1-3 m | Legacy ear-to-ear |
| 60 GHz | tens of mW | multi-Gbit/s | short LoS | High-rate connectors |
Typical device power refers to two-way powered devices unless noted. NFC row reflects reader/endpoint power asymmetry.
Available products and roadmap
View Full Roadmap →XA-NFE2001
- Sub-milliwatt device power at 5 Mbit/s
- < 1 ms latency
- Key interface: SPI
XA-NFE3001
- <5mW power at 20Mbit/s
- < 0.2 ms latency
- Key interfaces: QSPI, CSI
Frequently Asked Questions
Looking for more? View all frequently asked questions about Wi-R at our resources hub.
NFE couples two powered devices using a contained electric field. It is designed for touch‑to‑arm’s‑length workflows where you want deterministic, low‑power links without room‑scale broadcast. Use it instead of NFC when you want higher throughput and lower device‑side power, and instead of NFMI or 60 GHz when you want sub‑milliwatt budgets at near‑field range.
Ready to explore NFE?