
Research Publications
Explore our latest research papers, technical publications, and scientific contributions in the field of Wi-R technology and semiconductor innovations.
Featured Research
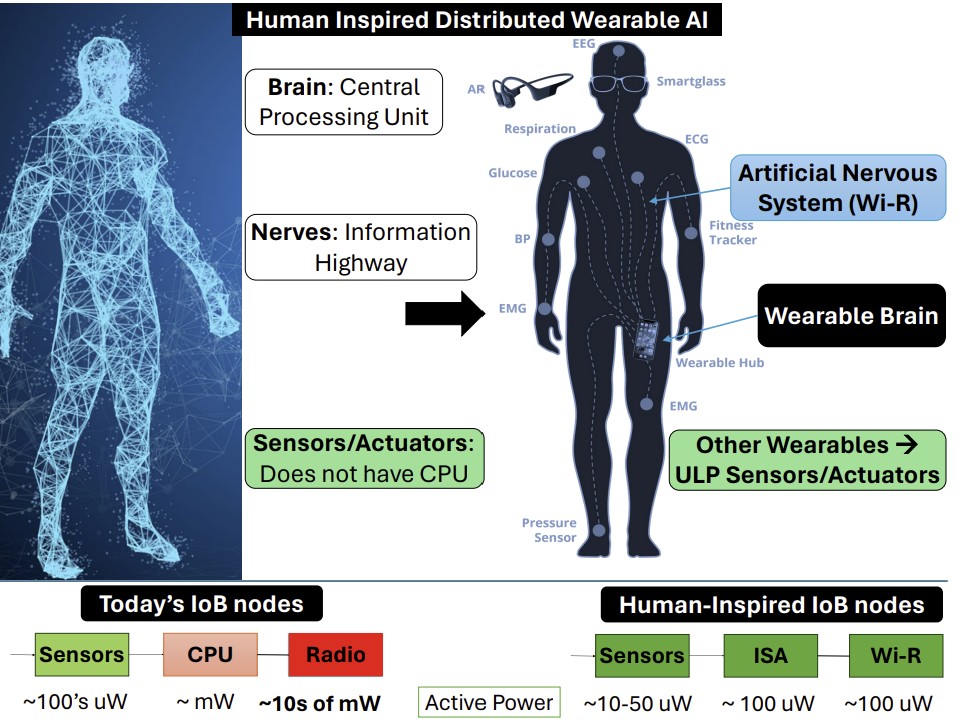
Human-Inspired Distributed Wearable AI
This paper delves into the vision for wearable AI technology, addressing the technical bottlenecks that stand in the way of its promised advancements.
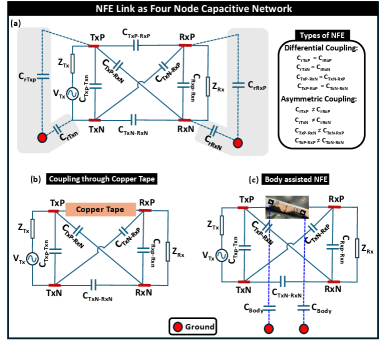
Near Field Electric (NFE): Energy-efficient, High-speed Communication at Decimeter-range
This paper introduces the physics of Wi-R NFE communication including testing results with Ixana chip
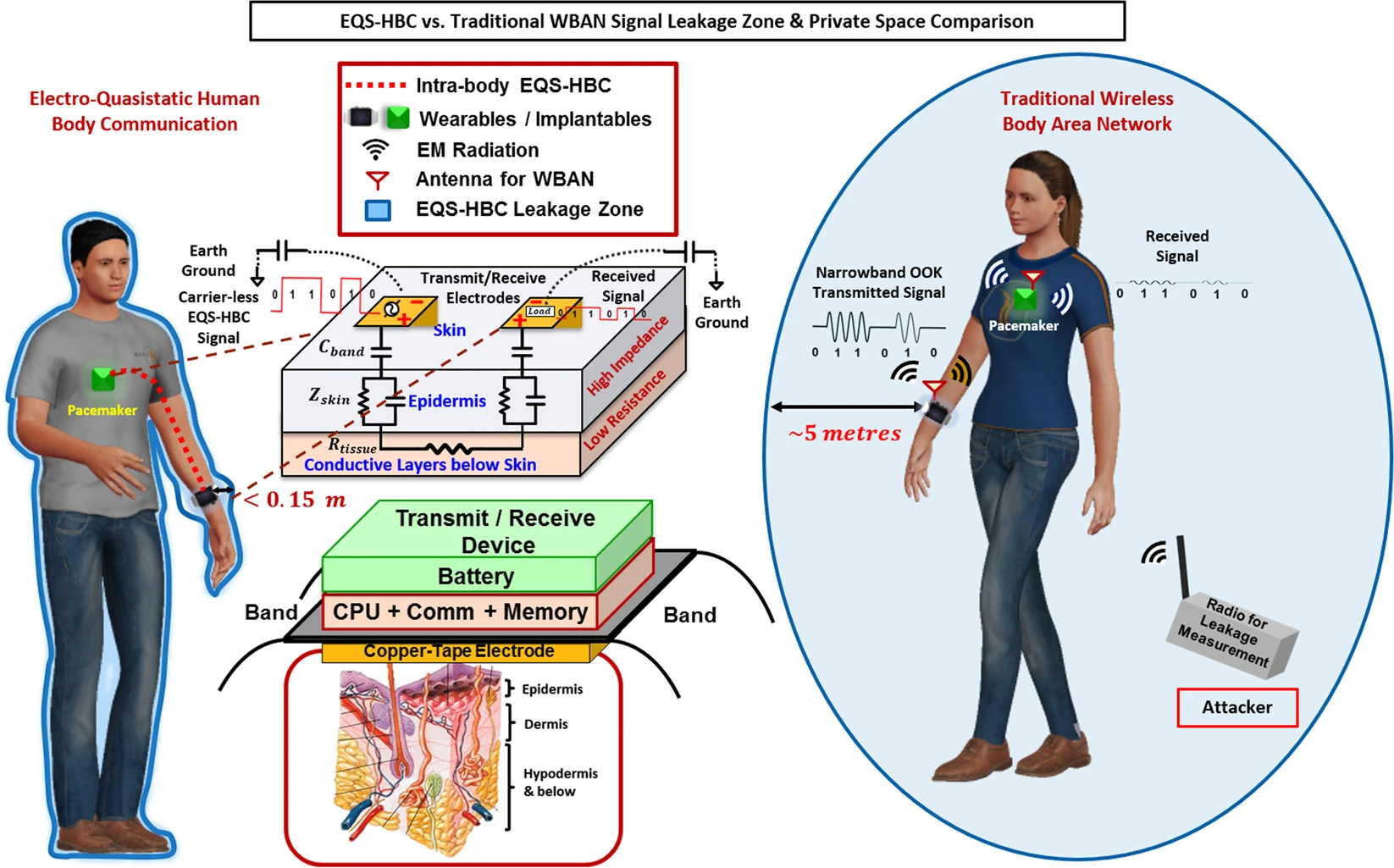
Enabling Covert Body Area Network using Electro-Quasistatic Human Body Communication
This Nature paper presents the physics Wi-R: of Electro-Quasistatic Human Body Communication (EQS-HBC), a method for localizing signals around the wearer, thereby making it extremely difficult for a nearby eavesdropper to intercept critical private data, thus producing a covert communication channel.
Selected Publications
A 65nm 21.9 pJ/Sa Pixel to PWM Conversion SoC with Time-domain Body Communication for ULP Body-Worn Video Sensor Nodes with Distributed Real-Time Inference
Gourab Barik, Baibhab Chatterjee, Gaurav Kumar, Shreyas Sen
|April 21, 2024Presented at the 2024 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), this paper introduces a novel system-on-chip (SoC) for ultra-low-power body-worn video sensor nodes. The solution enables efficient video sensing, computing, and communication with minimal energy consumption, addressing the growing demand for long-term wearable devices in the Internet of Bodies (IoB) and Internet of Things (IoT) era.
Inter-body coupling in electro-quasistatic human body communication: theory and analysis of security and interference properties
Mayukh Nath, Shovan Maity, Shitij Avlani, Scott Weigand, Shreyas Sen
|February 23, 2021This study investigates the security and interference properties of Electro-quasistatic Human Body Communication (EQS-HBC), which utilizes the human body's conductive properties for secure communication. The research presents a novel attack method for EQS-HBC devices and analyzes the system's resilience, showing that signals are contained within 1cm of the body surface and 15cm from the EQS-HBC device, significantly reducing the risk of eavesdropping compared to traditional wireless communication.
Physically Secure Wearable–Wearable Through-Body Interhuman Body Communication
David Yang, Shovan Maity, Shreyas Sen
|February 3, 2022This research presents BodyWire, an electro-quasistatic Human Body Communication (EQS-HBC) system enabling secure communication between wearable devices. The study characterizes human body channel loss across various environments, postures, and body locations, demonstrating signal confinement close to the body for enhanced security. The work includes the first through-body interhuman channel loss characterization and presents a secure interhuman information exchange prototype with the smallest form factor HBC demonstration to date.
A 65nm 63.3µW 15Mbps Transceiver with Switched-Capacitor Adiabatic Signaling and Combinatorial-Pulse-Position Modulation for Body-Worn Video-Sensing AR Nodes
Baibhab Chatterjee, Arunashish Datta, Mayukh Nath, Gaurav Kumar K, Nirmoy Modak, Shreyas Sen
|February 20-26, 2022This paper presents a low-power transceiver for body-worn video-sensing AR nodes, featuring switched-capacitor adiabatic signaling and combinatorial-pulse-position modulation. The design achieves 15Mbps data transfer with only 63.3µW power consumption, addressing the challenge of high-speed data transfer among wearable devices with ultra-low power consumption. The solution overcomes limitations of traditional Human-Body Communication (HBC) transmitters by reducing power consumption associated with plate-to-plate capacitance.
Bioelectronic Sensor Nodes for the Internet of Bodies
Baibhab Chatterjee, Pedram Mohseni, Shreyas Sen
|June 2023This review article in the Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering explores the development and implementation of bioelectronic sensor nodes for the Internet of Bodies (IoB). It discusses the technological advancements, challenges, and future directions in creating interconnected, intelligent sensor networks for continuous health monitoring and personalized healthcare applications.
IoB: The Vision of the Internet of Bodies
Arunashish Datta, Shreyas Sen
|August 6, 2023This paper explores the concept of the Internet of Bodies (IoB), which represents the confluence of miniaturized electronic devices in and around the human body that communicate and share information to improve their collective performance. The study examines the technological landscape of IoB, current challenges, and future possibilities for human empowerment through body-area networks and ubiquitous computing.
Biphasic quasistatic brain communication for energy-efficient wireless neural implants
Baibhab Chatterjee, Mayukh Nath, Gaurav Kumar K, Shulan Xiao, Krishna Jayant, Shreyas Sen
|September 2023This paper introduces biphasic quasistatic brain communication for wireless neural implants, offering an energy-efficient alternative to traditional electromagnetic, ultrasound, optical, and magneto-electric methods. The approach utilizes electro-quasistatic signaling with minimal end-to-end channel loss (60 dB at 55mm) through dipole-coupling-based signal transfer in brain tissue. The system includes a series capacitor to block DC current and maintain ion balance, making it suitable for long-term neural implants.
Human-structure and human-structure-human interaction in electro-quasistatic regime
Samyadip Sarkar, David Yang, Mayukh Nath, Arunashish Datta, Shovan Maity, Shreyas Sen
|February 18, 2025This paper explores electroquasistatic body-coupled communication, utilizing conductive structures for human-structure and human-structure-human interactions. It demonstrates fast setup communication specificity and lower path loss during touch, with potential applications in Human-Machine Interaction and assistive technology.
Human body communication transceivers
Qi Huang, Abdelhay Ali, Abdulkadir Celik, Gianluca Setti, Jaafar Elmirghani, Noha Al-Harthi, Khaled N. Salama, Shreyas Sen, Mohammed E. Fouda, Ahmed M. Eltawil
|March 24, 2025This review article discusses the transformative potential of the Internet of Bodies (IoB) in healthcare, focusing on human body communication (HBC) as a key enabling technology. It covers the progress in HBC transceivers, their role in biomedical applications, and the integration of wearable, implantable, ingestible, and injectable devices for seamless connectivity in healthcare solutions.
Touchscreen communication (ToSCom): Electro-Quasistatic body communication during touch sensing
Arunashish Datta, David Yang, Shovan Maity, Shreyas Sen
|March 24, 2025This work introduces Touchscreen Communication (ToSCom), a high-speed (>Mbps) simultaneous communication and touch sensing interface. It enables communication through touchscreens during touch events, allowing for personalized user-specific account data access. The paper demonstrates a low path loss channel across the entire touchscreen surface enabling 3 Mbps data rate communication with minimal bit-error-rate.
Electro-quasistatic and resonant cavity car body communication
David Yang, Shreyas Sen
|May 21, 2025This work introduces EQS car body communication, recognizing the potential of the car's chassis as a medium to confine EQS fields. This alternative approach offers a new modality for efficient intra-vehicle wireless communication, addressing power efficiency and physical security concerns. Furthermore, this research demonstrates that a vehicle can be treated as a resonant cavity, providing low-loss, wideband channels for high-speed communication.
On the Safety of Human Body Communication
Shovan Maity, M. Nath, G. Bhattacharya, Baibhab Chatterjee, Shreyas Sen
|April 13, 2020This paper analyzes the safety aspects of Human Body Communication (HBC) by examining the compliance of current density and electric/magnetic fields with established safety standards. It includes circuit and Finite Element Method (FEM) based simulations to quantify safety compliance.
Sub-μWRComm: 415-nW 1–10-kb/s Physically and Mathematically Secure Electro-Quasi-Static HBC Node for Authentication and Medical Applications
Shovan Maity, Nirmoy Modak, Mayukh Nath, Debayan Das, Shreyas Sen
|Jan 20, 2021This article presents the first >1 kb/s Sub-μW WeaRable Communication (Sub-μWRComm) node, which uses EQS-HBC for physical security and an AES-256 engine for mathematical security, operating at sub-μW power budget. The solution enables secure communication for applications like authentication and medical monitoring while confining signals within close proximity to the body.
Turning the Body Into a Wire
Shovan Maity, Debayan Das, Shreyas Sen
|Nov 24, 2020This IEEE Spectrum article explores how using the human body as a communications channel can enhance security. It discusses the vulnerabilities of wireless medical devices, referencing real-world examples including Dick Cheney's pacemaker security concerns and Barnaby Jack's demonstrations of hacking insulin pumps and pacemakers. The article highlights the potential of body-based communication to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive health data and connected devices.